
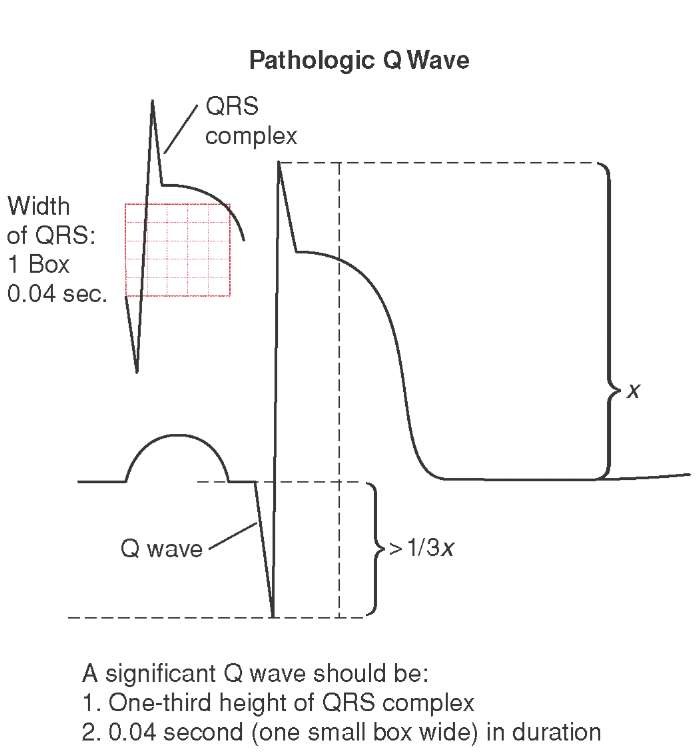
The pathological basis of QWs has mainly been studied through autopsy and animal experiments ( 9- 11). Clinical studies suggest that pathological QW on ECG is highly related to infarct size and extent of subendocardial infarction ( 6- 8). Previous work demonstrated an inconsistent relationship between QWs and infarction transmurality ( 4, 5). The traditional view that infarction transmurality correlates with the presence of QW has been challenged ( 1). The presence of pathological Q-wave (QW) on ECG is considered an important indicator of previous MI, and MIs with QW portend worse prognosis compared to non-Q-wave (NQW) infarctions ( 3). MR is capable of detecting small areas of infarction that may not be detected by ECG ( 1, 2). The electrocardiogram (ECG) is the most commonly used method for clinical diagnosis of MI because of its speed, convenience, and practicality. Identification of myocardial infarction (MI) is critical for determination of prognosis and treatment. The larger MI% was displayed in BB-LGE than in Conv-LGE in both QW group and NQW group (24.2☑0.3 vs. BB-LGE detected more subendocardial infarcted segments in the QW group and NQW group (Z=−4.24, P<0.001 Z=−5.57, P<0.001). Compared to Conv-LGE, BB-LGE provided higher CNR and SIR between infarcted myocardium and blood pool (6.3☒.6 vs. Using BB-LGE there were significant differences in detecting subendocardial infarcts in QW and NQW cohorts (Z=−5.85, P<0.001). For the NQW cohort, both sequences classified infarcts as transmural in 16/33 (48%) subjects and subendocardial in 17/33 (52%). For the QW cohort, both sequences classified infarcts as transmural in 21/23 (91%) subjects and subendocardial in 2/23 (9%). Fifty-six subjects were enrolled in the final analysis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
